The term Dutch Disease is an economic term that refers to the negative consequences that can arise from a sharp increase in a country’s income, especially from natural resources like oil, gas, or minerals. It usually leads to a strengthening of the country’s currency, which makes other sectors of the economy — like manufacturing or agriculture — less competitive in international markets. This can cause deindustrialization, job losses, and long-term economic imbalance.
The term Dutch Disease is an economic term that refers to the negative consequences that can arise from a sharp increase in a country’s income, especially from natural resources like oil, gas, or minerals. It usually leads to a strengthening of the country’s currency, which makes other sectors of the economy — like manufacturing or agriculture — less competitive in international markets. This can cause deindustrialization, job losses, and long-term economic imbalance.
🔍 Origin of the Term “Dutch Disease”
- The term was first used in 1977 by The Economist magazine.
- It described the economic problems faced by the Netherlands after the discovery of natural gas in the North Sea in the 1960s.
- The gas exports led to large inflows of foreign currency, which appreciated the Dutch guilder, making Dutch manufactured goods more expensive and less competitive internationally.
- As a result, the Dutch manufacturing sector declined, despite the boom in the energy sector.
💡 Key Features of Dutch Disease:
- Resource Boom (e.g., oil, gas, minerals)
- Currency Appreciation (stronger exchange rate)
- Decline in Other Export Sectors (especially manufacturing)
- Shift in Labor and Investment toward the booming resource sector
- Economic Imbalance and vulnerability to commodity price swings
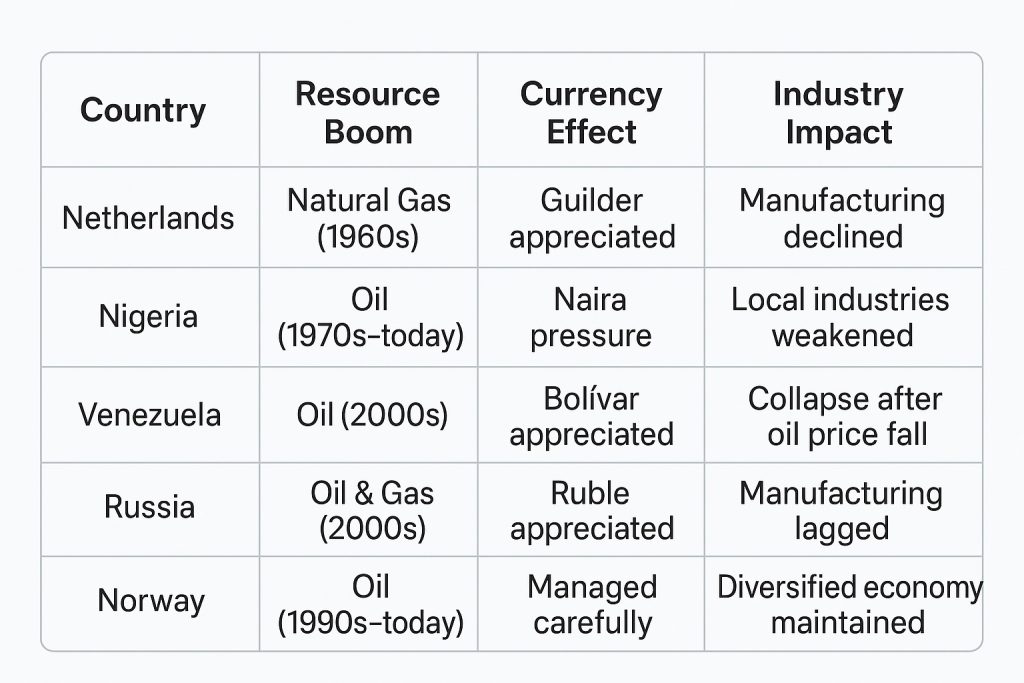
🌍 Real-World Examples:
- Nigeria and Venezuela with oil exports
- Russia (oil and gas)
- Australia (mining boom)
Great — let’s break it down thoroughly with:
- A diagram to visually explain Dutch Disease
- Step-by-step numerical examples using real or simplified data
- Several country examples with actual economic figures
📊 1. Diagram: Dutch Disease Explained
Here’s a simplified flow diagram showing the chain reaction:
Discovery of Natural Resources
⬇
Export Boom (e.g., oil, gas)
⬇
Inflow of Foreign Currency Increases
⬇
Appreciation of Domestic Currency
⬇
⛔ Exported Goods Become More Expensive
⛔ Manufacturing & Agriculture Decline
⬇
Economy Becomes Resource-Dependent
⬇
Vulnerable to Commodity Price Shocks
📐 2. Numerical Example: How Dutch Disease Works
Let’s say a country called Resourceland discovers oil.
📌 Initial State:
- Exports:
- Oil: $5 billion
- Manufactured goods: $10 billion
- Exchange rate: 1 Resourle = 1 USD
📌 After Oil Boom:
- Oil exports increase to: $25 billion
- Total exports now: $35 billion
👉 Currency appreciates:
- Inflow of dollars causes exchange rate to change from:
- 1 Resourle = 1 USD to 1 Resourle = 1.5 USD
📉 Impact on Manufacturing:
- Previously, a product costing 100 Resourles = $100
- Now, 100 Resourles = $150 in foreign markets — too expensive
- Foreign buyers switch to cheaper products from other countries
- Manufacturing exports fall from $10 billion to $6 billion
🌍 3. Real-World Country Examples
🇳🇱 Netherlands (1960s)
- Gas field discovery in Groningen
- Dutch guilder appreciated
- Manufacturing sector shrank
- Term “Dutch Disease” was coined in 1977 by The Economist
🇳🇬 Nigeria
- Oil accounts for 90% of exports, but:
- Manufacturing GDP share fell from 8% (1980s) to less than 5% (2010s)
- Currency appreciation made local industries uncompetitive
- Heavy reliance on imports for basic goods
🇻🇪 Venezuela
- Oil: ~95% of exports
- Boost in oil prices (2000s): strong bolívar
- Domestic industries collapsed
- When oil prices fell in 2014, the economy went into hyperinflation and collapse
🇷🇺 Russia
- Resource-driven economy (oil & gas ~60% of exports)
- Ruble appreciated during high oil prices
- Manufacturing sector lagged
- 2014 oil price drop + sanctions caused severe recession
🇳🇴 Norway (Managed it Well!)
- Oil-rich but avoided Dutch Disease by:
- Creating a sovereign wealth fund (Government Pension Fund)
- Investing oil profits abroad
- Preventing domestic currency from overheating